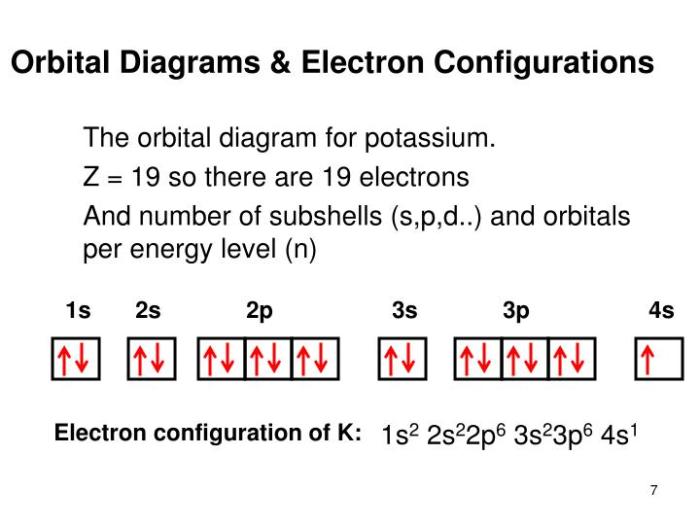
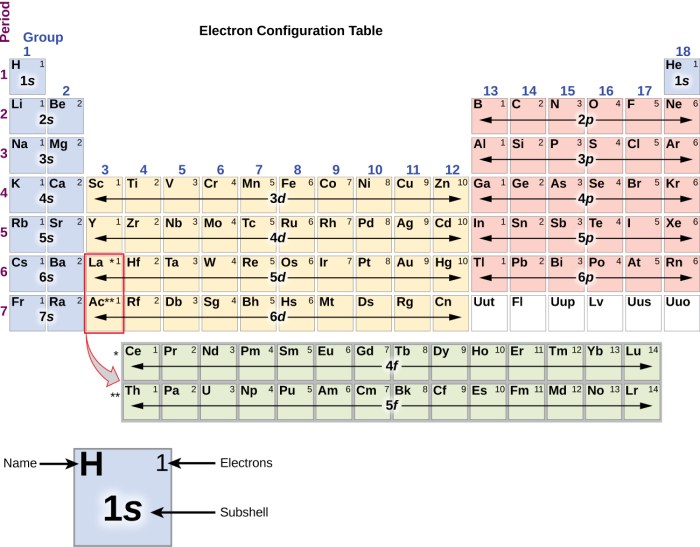
Identify the element that corresponds to the orbital diagram – Identifying the element that corresponds to the orbital diagram is a crucial skill in chemistry. It provides valuable insights into the electronic structure and properties of elements, facilitating a deeper understanding of their chemical behavior.
This comprehensive guide delves into the concepts of orbital diagrams, their significance, and the techniques for identifying elements from them. It also explores variations in orbital diagrams and their applications in predicting chemical properties and understanding molecular bonding.
Orbital Diagrams: Identify The Element That Corresponds To The Orbital Diagram
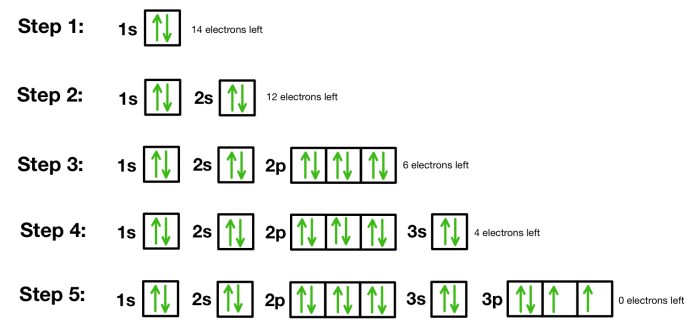
Orbital diagrams are visual representations of the electron configuration of an atom or molecule. They provide information about the number, energy, and spatial distribution of electrons within the atom or molecule. Orbital diagrams are essential tools for understanding chemical bonding and predicting the properties of elements and compounds.
Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams, Identify the element that corresponds to the orbital diagram
The electron configuration of an atom or molecule describes the arrangement of electrons in its orbitals. Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, and the energy of the orbital determines the electron’s distance from the nucleus. Orbital diagrams use arrows to represent electrons, with the direction of the arrow indicating the electron’s spin.
Aufbau Principle and Hund’s Rule
The Aufbau principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. Hund’s rule states that when filling orbitals of equal energy, electrons will occupy separate orbitals with parallel spins before pairing up. These principles help determine the electron configuration and orbital diagram of an atom or molecule.
Identifying Elements from Orbital Diagrams
To identify an element from an orbital diagram, follow these steps:
- Count the total number of electrons represented in the diagram.
- Use the periodic table to find the element with the atomic number that matches the number of electrons.
- Compare the orbital diagram to the known electron configuration of the element to confirm the identification.
Variations in Orbital Diagrams
Different types of orbital diagrams exist:* Ground state diagramsrepresent the lowest energy configuration of an atom or molecule.
- Excited state diagramsrepresent configurations with higher energy than the ground state.
- Molecular orbital diagramsrepresent the electron distribution in molecules, showing the bonding and antibonding orbitals.
Applications of Orbital Diagrams
Orbital diagrams are used in chemistry to:* Predict chemical properties and reactivity.
- Understand chemical bonding and molecular structure.
- Design and develop new materials and compounds.
- Explain the behavior of electrons in atoms and molecules.
Query Resolution
What is an orbital diagram?
An orbital diagram is a visual representation of the distribution of electrons in an atom or molecule. It shows the shape, energy level, and spin of each electron.
How can I identify the element from an orbital diagram?
To identify the element from an orbital diagram, count the total number of electrons and refer to the periodic table. The element with the corresponding atomic number is the correct identification.
What is the significance of orbital diagrams?
Orbital diagrams provide insights into the chemical properties and reactivity of elements. They help predict bonding behavior, molecular structure, and various other aspects of chemical systems.