Nids is an advanced version of nips. – NIDS is an advanced version of NIPS, representing a significant leap forward in the realm of network security. NIDS boasts enhanced capabilities that empower organizations with robust protection against a wide spectrum of cyber threats.
This innovative technology offers advanced detection and prevention mechanisms, allowing for the identification and mitigation of network threats with greater precision and efficiency.
NIDS Advanced Capabilities
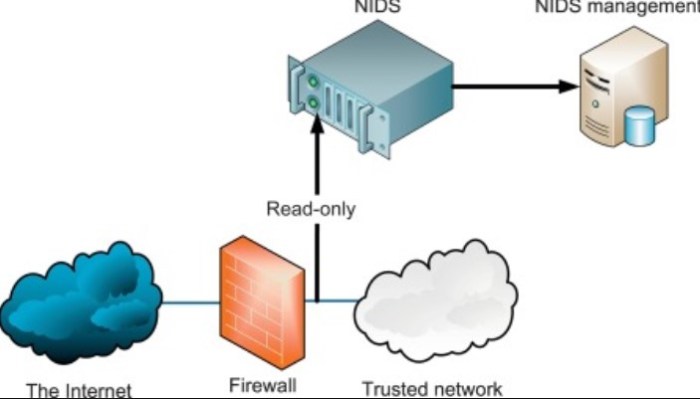
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) have evolved significantly from their predecessors, Network Intrusion Prevention Systems (NIPS), offering advanced capabilities that enhance network security.
NIDS employ sophisticated algorithms and techniques to analyze network traffic patterns, identify anomalies, and detect potential threats. Unlike NIPS, which primarily focus on blocking malicious traffic, NIDS provide a more comprehensive approach to network security by monitoring and analyzing traffic in real-time.
Advanced Features of NIDS
- Signature-based detection:NIDS use predefined signatures to identify known threats, such as malware, viruses, and exploits.
- Anomaly-based detection:NIDS analyze traffic patterns and identify deviations from normal behavior, which may indicate an attack.
- Stateful inspection:NIDS track the state of network connections and use this information to detect suspicious behavior, such as unexpected port scans or out-of-sequence packets.
- Protocol analysis:NIDS inspect network protocols, such as TCP, UDP, and ICMP, to identify potential vulnerabilities and attacks.
- Behavioral analysis:NIDS analyze user and system behavior to detect suspicious activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration.
Benefits of Using NIDS over NIPS
- Enhanced detection capabilities:NIDS provide a more comprehensive view of network traffic and can detect a wider range of threats compared to NIPS.
- Proactive monitoring:NIDS monitor traffic in real-time, allowing organizations to identify potential threats before they cause damage.
- Reduced false positives:NIDS use advanced techniques to minimize false positives, ensuring that security teams focus on genuine threats.
- Improved threat intelligence:NIDS collect valuable information about threats and can be used to improve security posture and inform threat intelligence.
Detection and Prevention Mechanisms: Nids Is An Advanced Version Of Nips.
Network intrusion detection systems (NIDS) employ a range of detection and prevention mechanisms to identify and respond to network threats. These mechanisms leverage signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and other advanced techniques to protect networks from malicious activity.
Signature-based detection involves matching network traffic against a database of known attack signatures. When a match is found, the NIDS raises an alert and takes appropriate action, such as blocking the traffic or sending a notification to the network administrator.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection analyzes network traffic patterns to identify deviations from normal behavior. By establishing a baseline of expected network behavior, NIDS can detect and alert on unusual traffic patterns that may indicate an attack or compromise.
NIDS also employs additional techniques such as heuristic analysis, protocol decoding, and stateful inspection to enhance detection capabilities. These techniques enable NIDS to identify complex attacks that may evade signature-based detection.
Common Attack Types
NIDS can detect and mitigate a wide range of common attack types, including:
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks
- Port scans
- Buffer overflows
- Malware infections
- Phishing attacks
Deployment and Configuration

Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) require careful deployment and configuration to ensure optimal performance and effectiveness in a network environment.
Sensor Selection and Placement
The choice and placement of NIDS sensors are critical. Sensors should be strategically positioned to monitor network traffic at key points, such as network perimeters, internal segments, and critical servers. The type of sensor used should align with the specific network environment and security requirements.
Tuning and Customization
NIDS settings should be meticulously tuned and customized to optimize detection capabilities and minimize false positives. This involves adjusting parameters such as signature updates, threshold values, and detection algorithms. Proper tuning ensures that the NIDS can effectively detect malicious activity without overwhelming the system with excessive alerts.
Integration and Interoperability
Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) can be effectively integrated with various security tools and systems to enhance their overall security posture. This integration allows for a more comprehensive and coordinated approach to threat detection, prevention, and response.
One key aspect of NIDS integration is its ability to share information with other security systems, such as firewalls, intrusion prevention systems (IPS), and security information and event management (SIEM) systems. By sharing threat intelligence and event data, these systems can work together to provide a more complete picture of the network’s security posture and respond to threats more effectively.
Successful NIDS Integrations, Nids is an advanced version of nips.
Several successful NIDS integrations have been implemented in practice, demonstrating the benefits of interoperability:
- Integration with Firewalls:NIDS can be integrated with firewalls to provide real-time threat detection and prevention. The NIDS can monitor network traffic and identify suspicious patterns or attacks, which can then be blocked by the firewall.
- Integration with IPS:NIDS can be integrated with IPS to provide proactive threat prevention. The NIDS can detect potential attacks and send alerts to the IPS, which can then take appropriate actions, such as dropping malicious packets or blocking connections.
- Integration with SIEM:NIDS can be integrated with SIEM systems to provide centralized logging and analysis of security events. The NIDS can send alerts and event data to the SIEM, which can then be used for threat detection, incident response, and forensic analysis.
Challenges and Considerations
While NIDS integration offers significant benefits, it also presents several challenges and considerations:
- Interoperability Standards:Ensuring interoperability between NIDS and other security systems can be challenging due to the lack of standardized protocols and interfaces. This can make it difficult to integrate NIDS with different vendor solutions.
- Data Exchange:The exchange of data between NIDS and other systems can be complex and resource-intensive. It is important to optimize data exchange mechanisms to avoid performance degradation.
- Configuration and Management:Integrating NIDS with other systems requires careful configuration and management to ensure that they work together effectively. This includes setting up communication channels, defining data exchange formats, and resolving potential conflicts.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications

Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) have proven their effectiveness in protecting networks from a wide range of threats. Here are some case studies and real-world examples:
Early Detection of Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
NIDS has been instrumental in detecting and preventing APTs, which are sophisticated and targeted attacks that often remain undetected for long periods. By analyzing network traffic for anomalies and suspicious patterns, NIDS can identify malicious activity even before it reaches critical systems.
Protection against Zero-Day Attacks
NIDS can provide protection against zero-day attacks, which exploit vulnerabilities that are unknown to security vendors. By analyzing traffic patterns and comparing them against known attack signatures, NIDS can detect and block these attacks even before patches are available.
Detection of Insider Threats
NIDS can help detect insider threats, which can be difficult to identify through traditional security measures. By monitoring network traffic for unusual patterns or deviations from established baselines, NIDS can identify suspicious activities that may indicate malicious intent.
Lessons Learned and Best Practices
Case studies and real-world applications have highlighted the following lessons and best practices:
- Deploy NIDS in strategic locations throughout the network to maximize visibility and coverage.
- Configure NIDS to analyze all relevant traffic, including encrypted traffic if possible.
- Tune NIDS rules and signatures to minimize false positives and ensure accurate detection.
- Integrate NIDS with other security systems, such as firewalls and SIEMs, to enhance overall security posture.
- Regularly review NIDS logs and alerts to identify potential threats and take appropriate action.
Future Trends and Advancements
The field of Network Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS) is constantly evolving, with new trends and advancements emerging all the time. These advancements are shaping the future of network security by providing organizations with more effective ways to detect and prevent cyber threats.
One of the most significant trends in NIDS technology is the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI and ML algorithms can be used to analyze large volumes of network data in real time, identify patterns, and detect anomalies that may indicate a cyberattack.
This allows NIDS to be more proactive and to detect threats that may have been missed by traditional signature-based detection methods.
Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
NIDS are increasingly being integrated with SIEM systems. SIEM systems collect and analyze data from a variety of sources, including NIDS, firewalls, and intrusion prevention systems (IPS). This data can be used to provide a comprehensive view of the security posture of an organization and to identify potential threats.
FAQ
What are the key advantages of NIDS over NIPS?
NIDS offers enhanced detection capabilities, real-time analysis, and a wider range of customizable options, providing organizations with a more comprehensive and adaptable security solution.
How does NIDS contribute to improved network security?
NIDS empowers organizations with the ability to identify and respond to network threats in real-time, effectively preventing breaches and minimizing the impact of cyberattacks.
What are some common use cases for NIDS?
NIDS is widely employed in critical infrastructure protection, financial institutions, healthcare organizations, and government agencies, where the security of sensitive data and systems is paramount.