Flinch or gasp in response – When the unexpected strikes, our bodies respond involuntarily with a flinch or a gasp. These reactions, often triggered by sudden stimuli, offer a glimpse into the intricate workings of our nervous system and the emotions that drive us. Embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of flinching and gasping, their physiological manifestations, and their profound implications.
From the physical changes that prepare us for defense to the psychological responses that reveal our inner states, this exploration delves into the fascinating world of these involuntary reactions. Join us as we uncover the cultural variations, health implications, and strategies for managing these behaviors, providing a comprehensive understanding of how our bodies and minds respond to the unexpected.
Initial Reaction and Causes
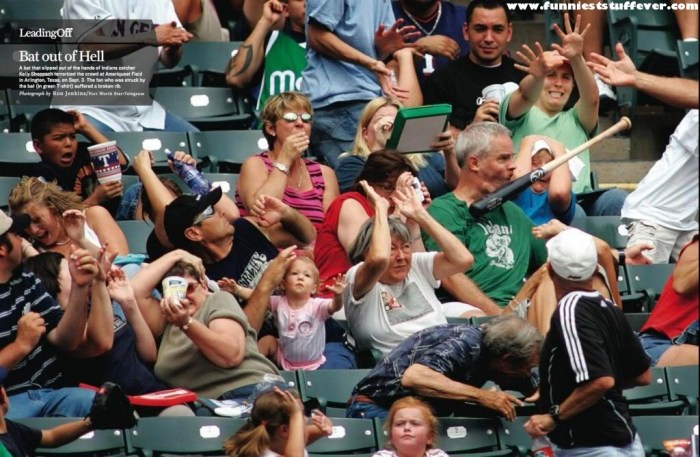

Flinching and gasping are involuntary reactions that occur in response to unexpected or threatening stimuli. These responses are mediated by the nervous system and are designed to protect the individual from harm.
Common Stimuli
Some common stimuli that can trigger a flinch or gasp include:
- Loud noises
- Sudden movements
- Painful stimuli
- Surprises
- Threats
Role of the Nervous System
When a stimulus is detected by the senses, it is transmitted to the spinal cord and then to the brain. The brain then sends a signal back to the muscles, causing them to contract and produce the flinch or gasp response.
The nervous system is responsible for the rapid and automatic nature of these responses. This allows the individual to react quickly to danger and protect themselves from harm.
Physiological Manifestations

Flinching and gasping are physical responses to sudden stimuli that prepare the body for defense or protection. These responses involve a series of physiological changes that occur in the body.
When a sudden stimulus is detected, the body’s sympathetic nervous system activates the “fight-or-flight” response. This response triggers a cascade of physiological changes that prepare the body for action.
Flinching
Flinching is a sudden, involuntary muscle contraction that occurs in response to a perceived threat. This response is mediated by the spinal cord and involves the contraction of muscles in the neck, shoulders, and arms.
Flinching helps to protect the body from harm by moving the head and body away from the perceived threat. It also tenses the muscles in the neck and shoulders, which can help to protect the head and spine from injury.
Gasping
Gasping is a sudden, involuntary inhalation of air that occurs in response to a sudden stimulus. This response is mediated by the respiratory center in the brain and involves the contraction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
Flinching or gasping in response to a sudden stimulus is a natural reflex, but did you know that the way you react can be influenced by your language? In certain languages, such as those with suffixes with soft or “china” sounds , people tend to flinch or gasp with a more gentle, subtle motion, as if they’re trying to soften the impact of the surprise.
Gasping helps to increase the oxygen supply to the body, which is necessary for the “fight-or-flight” response. It also helps to clear the airway of any obstructions, which can improve breathing.
Psychological Implications
Flinching or gasping in response to a stimulus can have significant psychological implications. These reactions often indicate a range of emotions and cognitive processes, providing insights into an individual’s emotional state and cognitive functioning.
Emotional Responses
Flinching or gasping can be a manifestation of fear or surprise. Fear is an emotional response to a perceived threat, and it is often accompanied by physical reactions such as increased heart rate, sweating, and muscle tension. Flinching is a common physical response to fear, as it is an involuntary reaction to a perceived danger.
Surprise, on the other hand, is an emotional response to an unexpected event. It is often accompanied by feelings of excitement, astonishment, or even confusion. Gasping is a common physical response to surprise, as it is an involuntary reaction to a sudden or unexpected stimulus.
Cognitive Responses
In addition to emotional responses, flinching or gasping can also be indicative of cognitive processes. For example, flinching can be a sign of hypervigilance, which is a state of heightened awareness and alertness. Hypervigilance is often associated with anxiety disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), where individuals may experience exaggerated startle responses to stimuli that remind them of a traumatic event.
Gasping, on the other hand, can be a sign of cognitive dissonance, which is a state of psychological discomfort that occurs when an individual holds two or more conflicting beliefs or attitudes. Gasping can be a physical manifestation of the cognitive effort required to reconcile these conflicting thoughts or beliefs.
Cultural and Contextual Factors

Flinching and gasping behaviors are not universal and can vary significantly across cultures and contexts. Social norms, expectations, and cultural values play a crucial role in shaping how people express these responses.
In some cultures, flinching or gasping may be seen as a sign of weakness or vulnerability, while in others, it may be considered a natural and acceptable response to unexpected stimuli.
Social Norms and Expectations
Social norms and expectations can influence how people express flinching or gasping behaviors. For example, in cultures where stoicism is valued, individuals may be expected to suppress these responses, while in more expressive cultures, they may be encouraged to express them more freely.
Cultural Values, Flinch or gasp in response
Cultural values can also shape flinching and gasping behaviors. In cultures that emphasize individualism, people may be more likely to express these responses as a way of asserting their personal boundaries, while in collectivist cultures, they may be more likely to suppress them in order to maintain harmony within the group.
Health Implications: Flinch Or Gasp In Response

Excessive or inappropriate flinching or gasping can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, ranging from anxiety disorders to neurological disorders.
If these behaviors become excessive or problematic, it’s important to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Potential Health Conditions Associated with Flinching or Gasping
- Anxiety disorders:Excessive flinching or gasping can be a symptom of anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder.
- Neurological disorders:Flinching or gasping can be a symptom of neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, and epilepsy.
- Thyroid disorders:Excessive flinching or gasping can be a symptom of thyroid disorders such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
- Vitamin B12 deficiency:Flinching or gasping can be a symptom of vitamin B12 deficiency.
- Caffeine overdose:Excessive caffeine intake can lead to flinching or gasping.
- Alcohol withdrawal:Flinching or gasping can be a symptom of alcohol withdrawal.
Management and Intervention

Flinching or gasping in response to certain stimuli can be managed or reduced through various strategies. These include techniques that address both the physical and psychological aspects of the behavior.
To mitigate the physical response, individuals can engage in relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga. These practices help calm the nervous system and reduce the startle response. Gradual exposure to the triggering stimuli in a controlled environment can also desensitize individuals and diminish the flinching or gasping reaction.
Role of Therapy
In cases where the underlying causes of these behaviors are complex or rooted in past experiences, therapy or counseling can play a crucial role. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used approach that helps individuals identify and challenge the negative thoughts and beliefs that contribute to the flinching or gasping response.
Through CBT, individuals learn coping mechanisms and strategies to manage their emotional reactions and reduce the severity of the behaviors.
Top FAQs
What causes flinching or gasping?
Flinching and gasping are involuntary reactions triggered by sudden or unexpected stimuli, such as loud noises, bright lights, or physical threats. These responses are mediated by the nervous system, which activates the body’s fight-or-flight response.
What are the physical changes that occur during flinching and gasping?
Flinching involves a rapid muscle contraction, often in the face or shoulders, while gasping is characterized by a sudden intake of breath. These responses prepare the body for defense or protection by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension.
How do flinching and gasping relate to emotions?
Flinching and gasping can be indicative of fear, surprise, or other strong emotions. These reactions are often associated with the amygdala, a brain region involved in processing emotions and triggering the fight-or-flight response.
Can flinching or gasping be a sign of an underlying health condition?
Excessive or inappropriate flinching or gasping can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions, such as anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or neurological disorders. If these behaviors become excessive or problematic, it is important to seek medical attention.